Key Takeaways

- Definition of 3D Printing: 3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that creates three-dimensional objects from digital files, employing materials like plastic, metal, or resin.
- Rapid Prototyping and Customization: The technology enables fast prototyping, allowing businesses to quickly test and modify their designs while offering customized products tailored to customer needs.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: 3D printing significantly reduces production costs and lead times by allowing for on-demand manufacturing, minimizing inventory expenses.
- Variety of Technologies: Different 3D printing methods, such as FDM, SLA, SLS, and DLP, cater to various applications, providing flexibility for businesses to select the most suitable technology.
- Applications Across Industries: 3D printing is transforming industries by enhancing manufacturing capabilities, creating personalized consumer products, and driving innovation in sectors like medical, automotive, and consumer goods.
- Challenges to Consider: Businesses must be aware of material limitations and regulatory concerns that can impact the effectiveness and compliance of 3D printing applications.
Imagine being able to create almost anything you can dream of right from your computer. That’s the magic of 3D printing. This innovative technology has transformed how we design and manufacture objects, allowing you to turn digital models into tangible items layer by layer. Whether it’s for prototyping, art, or even medical applications, 3D printing opens up a world of possibilities.
As you delve into the realm of 3D printing, you’ll discover how it’s reshaping industries and sparking creativity. From hobbyists crafting unique designs to businesses optimizing production processes, this technology is revolutionizing the way we think about making things. Get ready to explore the fascinating world of 3D printing and see how it can change your perspective on creation.
What Is 3D Printing?

3D printing refers to a process that creates three-dimensional objects from digital files. This technology builds items layer by layer, using materials like plastic, metal, or resin. By transforming digital designs into tangible products, 3D printing offers significant benefits for small businesses.
3D printing enables rapid prototyping, allowing you to test and modify designs quickly. You can create unique items specific to your customers’ needs, enhancing your competitive edge. Many small businesses leverage this technology to produce customized products, such as personalized gifts or specialty parts.
Adopting 3D printing reduces production costs and time. Instead of relying on traditional manufacturing methods, you can fabricate parts on-demand, minimizing inventory expenses. This flexibility allows you to respond swiftly to market changes.
Investing in 3D printing technology positions your small business at the forefront of innovation. It fosters creativity by enabling you to experiment with complex designs unattainable through conventional means. As you develop products that stand out, you also promote your brand’s uniqueness in the marketplace.
How 3D Printing Works
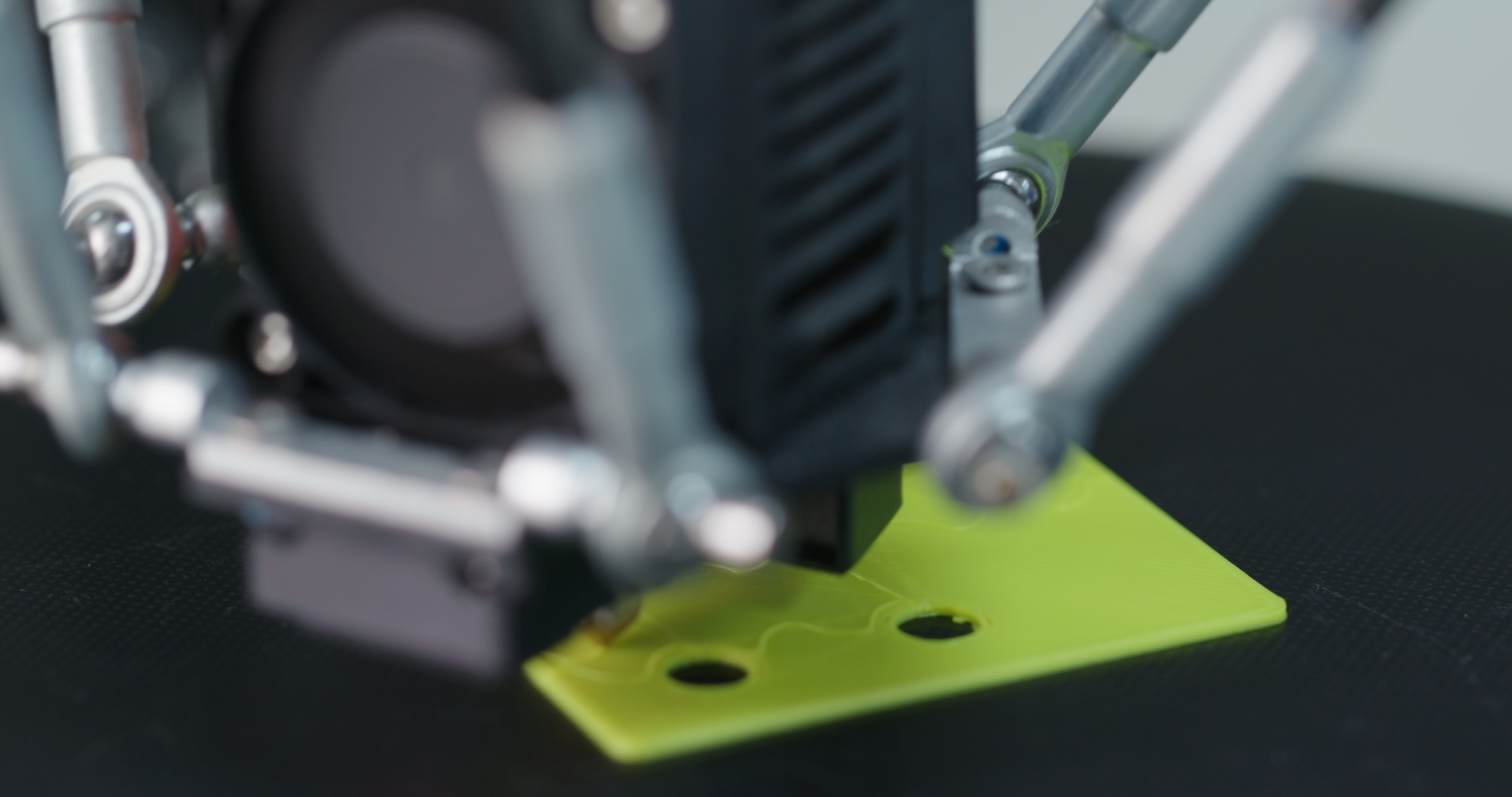
3D printing offers a streamlined process for transforming digital designs into tangible products. Understanding the steps involved can help small businesses leverage this technology effectively.
The 3D Printing Process
The 3D printing process begins with a digital model, often created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This model is converted into an STL file that communicates the design’s specifications to the printer. The printer then creates the object layer by layer, starting from the bottom and adding material until the complete object forms. Each layer represents a thinly sliced cross-section, ensuring precision and detail in the final product. This additive manufacturing method allows for easy adjustments and customizations, which can be particularly beneficial for small businesses looking to create unique prototypes or tailored products.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
Several 3D printing technologies exist, each suited for different applications and materials. Here are some of the most common types:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This method extrudes melted thermoplastic through a nozzle, forming layers as the material cools and hardens. FDM is widely used for prototyping due to its affordability and versatility.
- Stereolithography (SLA): SLA uses a UV laser to cure liquid resin layer by layer. This technology delivers high-resolution prints with complex geometries, making it ideal for detailed prototypes in small business applications.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS employs a laser to fuse powdered materials, such as nylon or metal, into solid structures. This technique allows for the creation of durable, functional parts, suitable for small businesses needing end-use products.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): Similar to SLA, DLP utilizes a digital light projector to cure resin. It produces high-speed prints with excellent surface quality, benefiting small businesses focused on efficiency.
Exploring these technologies enables you to determine which aligns best with your business needs, maximizing the potential of 3D printing in your operations.
Applications of 3D Printing

3D printing technology offers diverse applications that can significantly benefit small businesses. This process creates unique opportunities for innovation and efficiency in various industries.
Industrial Uses
3D printing revolutionizes industrial sectors by enabling rapid prototyping, reducing production times, and decreasing costs. You can create molds, tooling, and parts quickly, ensuring more efficient manufacturing processes. Companies like Ford and Boeing utilize 3D printing to produce complex components while minimizing material waste. Adopting this tech can enhance manufacturing capabilities, allowing you to respond swiftly to market demands and improve overall product quality.
Everyday Consumer Products
3D printing transforms how small businesses design and produce everyday consumer products. You can customize items like phone cases, jewelry, and home decor, offering personalized options that increase consumer engagement. Utilizing this technology empowers you to differentiate your offerings and meet specific customer preferences. Brands like Nike and Adidas use 3D printing for bespoke footwear, demonstrating the potential for innovation in consumer goods. Implementing 3D printing can expand your product range and attract a broader audience.
Benefits of 3D Printing

3D printing offers significant advantages for your small business, enhancing efficiency and creativity in product development.
Cost-Effectiveness
3D printing reduces manufacturing costs through on-demand production. Instead of maintaining large inventories, you can create items as needed, saving storage and material costs. The customizable nature of this tech allows you to produce low runs of specialized items without incurring hefty setup fees typical of traditional manufacturing methods. This approach leads to lower overheads, benefiting your bottom line significantly.
Customization and Flexibility
3D printing provides unparalleled customization options for your products. You can design unique items tailored to your customer’s specific needs, improving engagement and satisfaction. The flexibility of this technology enables quick adjustments to designs based on customer feedback or market trends, allowing you to adapt swiftly in a competitive landscape. With 3D printing, you can easily explore new designs and ideas, fostering innovation within your small business.
Challenges and Limitations

3D printing presents unique challenges and limitations that small businesses need to consider. Understanding these can help navigate potential pitfalls in adopting this technology.
Material Limitations
Material choices in 3D printing affect durability, strength, and application. Currently, options like plastic, metal, and resin dominate the market, but each material has specific properties. As a small business, consider that certain applications may require materials not yet well-suited for 3D printing, limiting functionality. For example, while Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) uses thermoplastics effectively, other materials may not provide the necessary strength or temperature resistance for specific designs. Assess your project needs carefully to ensure material compatibility with 3D printing technology.
Regulatory Concerns
Regulatory issues can pose significant challenges for small businesses utilizing 3D printing. Understanding regulations related to safety, intellectual property, and environmental standards is essential. Many products, especially in the medical and food sectors, require adherence to strict safety and quality guidelines. Stay informed about your local regulations and industry standards to prevent compliance issues that can arise from adopting new technology. Regularly consult with legal professionals familiar with 3D printing to navigate this landscape smoothly.
Awareness of these challenges will help you make informed decisions as you explore the opportunities that 3D printing technology offers for your small business.
Conclusion

3D printing is revolutionizing the way you think about design and production. Its ability to create customized products quickly and cost-effectively opens up new avenues for innovation in your business. Whether you’re in art, manufacturing, or retail, embracing this technology can set you apart from the competition.
As you explore the world of 3D printing, keep in mind the importance of selecting the right technology and materials for your specific needs. While challenges exist, the potential benefits far outweigh them. By staying informed and adaptable, you can harness the power of 3D printing to elevate your brand and engage your customers like never before.
Frequently Asked Questions
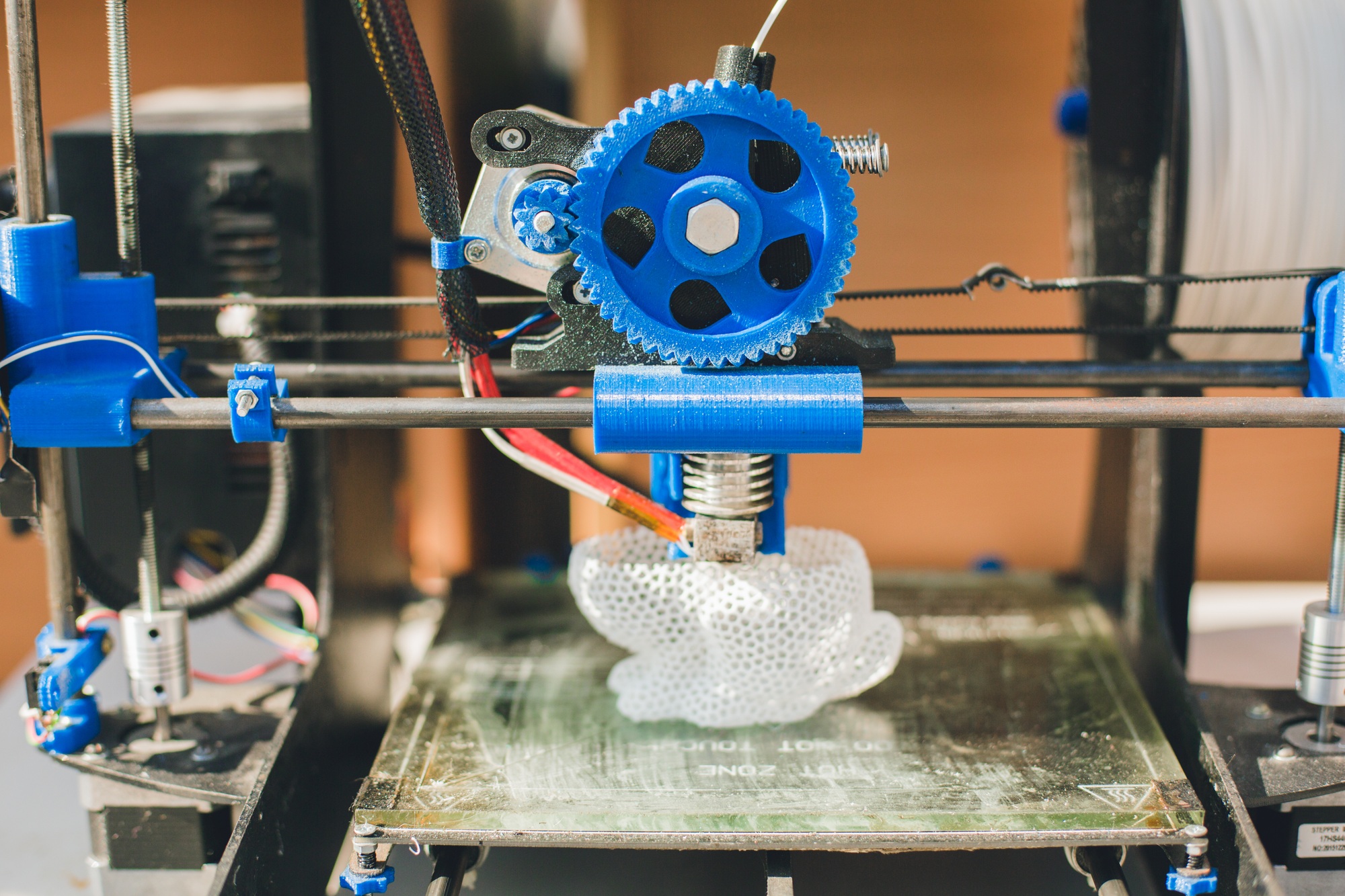
What is 3D printing?
3D printing is a manufacturing process that creates three-dimensional objects layer by layer from digital designs. It uses materials like plastic, metal, or resin to turn virtual models into physical items, greatly transforming industries such as prototyping, healthcare, and art.
How does 3D printing work?
3D printing starts with a digital model created using computer-aided design (CAD) software, converted into an STL file for the printer. The process, known as additive manufacturing, builds objects layer by layer, ensuring high precision and detail.
What are the benefits of 3D printing for small businesses?
Small businesses benefit from 3D printing through rapid prototyping, customization, and reduced costs. By enabling on-demand production, businesses can save on inventory expenses, respond quickly to market changes, and enhance brand identity with unique products.
What 3D printing technologies are available?
Popular 3D printing technologies include Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and Digital Light Processing (DLP). Each technology is suited for different applications and materials, allowing small businesses to choose the best fit for their needs.
What industries use 3D printing?
3D printing is used across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Companies like Ford and Boeing use it for rapid prototyping, while brands like Nike and Adidas employ it for customized footwear, showcasing the technology’s versatility.
What challenges do small businesses face with 3D printing?
Challenges include material limitations affecting durability and application, as well as regulatory concerns related to safety and intellectual property. Small businesses must understand these issues to make informed decisions while exploring 3D printing opportunities.
Image Via Envato: Chibelek, monkeybusiness, seventyfourimages, AnnaStills, Maria_Sbytova, leungchopan, kenishirotie, Mehaniq41



